About my projects, examples and tutorials
About my projects, examples and tutorials
Using the DrawArea class
This tutoral shows how to use the Gnome::Gtk4::DrawArea class. A drawing is made in a simple window where a few colored rectangles are shown.
As always, import the modules and make ourselfes comfortable with a few constants. We are using the Cairo module of Timo here.
use Cairo;
use Gnome::Glib::N-MainLoop:api<2>;
use Gnome::Gtk4::DrawingArea:api<2>;
use Gnome::Gtk4::Window:api<2>;
use Gnome::N::GlibToRakuTypes:api<2>;
use Gnome::N::N-Object:api<2>;
constant Window = Gnome::Gtk4::Window;
constant DrawingArea = Gnome::Gtk4::DrawingArea;
For this simple setup we need to use an event controller.
my Gnome::Glib::N-MainLoop $main-loop .= new-mainloop;
A simple helper class to stop the application
class SH {
method stopit () {
say 'close request';
$main-loop.quit;
}
}
Now we have to set a drawing function which does the drawing in the provided area. The user data and the destroy notifier function are not provided by using gpointers.
with my DrawingArea $draw .= new-drawingarea {
.set-draw-func( &drawit, gpointer, gpointer);
}
Put the drawing area in a window and display it using .present().
with my Window $window .= new-window {
.register-signal( SH.new, 'stopit', 'close-request');
.set-title('My Rectangles');
.set-size-request( 300, 300);
.set-child($draw);
.present;
}
Finally start the event loop
$main-loop.run;
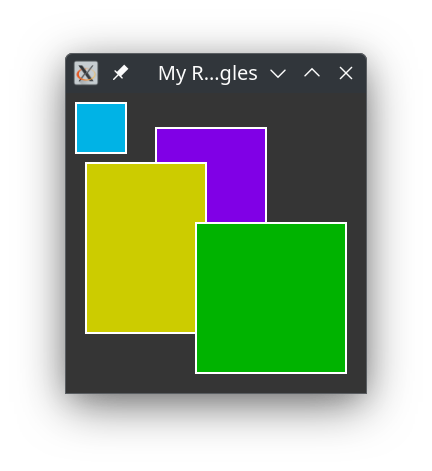
This subroutine will draw four rectangles with different colors. For the drawing commands you must look into the documentation of Cairo and documentation at the Cairo site.
sub drawit (
N-Object $d, Cairo::cairo_t $cr, gint $w, gint $h, gpointer $p
) {
with Cairo::Context.new($cr) {
.rgb(0, 0.7, 0.9);
.rectangle(10, 10, 50, 50);
.fill :preserve;
.rgb(1, 1, 1);
.stroke;
.rgb(0.5, 0.0, 0.9);
.rectangle(90, 35, 110, 110);
.fill :preserve;
.rgb(1, 1, 1);
.stroke;
.rgb(0.8, 0.8, 0);
.rectangle(20, 70, 120, 170);
.fill :preserve;
.rgb(1, 1, 1);
.stroke;
.rgb(0, 0.7, 0.0);
.rectangle(130, 130, 150, 150);
.fill :preserve;
.rgb(1, 1, 1);
.stroke;
};
}
With the following result;