Gnome::Gtk3::FileChooserButton
A button to launch a file selection dialog
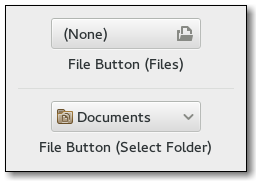
Description
The Gnome::Gtk3::FileChooserButton is a widget that lets the user select a file. It implements the Gnome::Gtk3::FileChooser interface. Visually, it is a file name with a button to bring up a Gnome::Gtk3::FileChooserDialog. The user can then use that dialog to change the file associated with that button. This widget does not support setting the select-multiple property to 1.
The Gnome::Gtk3::FileChooserButton supports the GtkFileChooserActions (from Gnome::Gtk3::FileChooser) GTK_FILE_CHOOSER_ACTION_OPEN and GTK_FILE_CHOOSER_ACTION_SELECT_FOLDER.
The Gnome::Gtk3::FileChooserButton will ellipsize the label, and will thus request little horizontal space. To give the button more space, you should call gtk_widget_get_preferred_size(), gtk_file_chooser_button_set_width_chars(), or pack the button in such a way that other interface elements give space to the widget.
Css Nodes
Gnome::Gtk3::FileChooserButton has a CSS node with name “filechooserbutton”, containing a subnode for the internal button with name “button” and style class “.file”.
See Also
Gnome::Gtk3::FileChooserDialog
Synopsis
Declaration
unit class Gnome::Gtk3::FileChooserButton;
also is Gnome::Gtk3::Box;
also does Gnome::Gtk3::FileChooser;
Inheriting this class
Inheriting is done in a special way in that it needs a call from new() to get the native object created by the class you are inheriting from.
use Gnome::Gtk3::FileChooserButton;
unit class MyGuiClass;
also is Gnome::Gtk3::FileChooserButton;
submethod new ( |c ) {
# let the Gnome::Gtk3::FileChooserButton class process the options
self.bless( :GtkFileChooserButton, |c);
}
submethod BUILD ( ... ) {
...
}
Example
Create a button to let the user select a file in /etc
use Gnome::Gtk3::FileChooser;
use Gnome::Gtk3::FileChooserButton;
my Gnome::Gtk3::FileChooserButton $button .= new(
:title('Select a file'), :action(GTK_FILE_CHOOSER_ACTION_OPEN)
);
$button.set-current-folder("/etc");
Methods
new
new( :title, :action)
Create a new FileChooserButton object.
multi method new (
Str :$title!, GtkFileChooserAction,
GtkFileChooserAction :$action = GTK_FILE_CHOOSER_ACTION_OPEN
)
[[gtk_] file_chooser_button_] get_title
Retrieves the title of the browse dialog used by button. The returned value should not be modified or freed.
Returns: a pointer to the browse dialog’s title.
method gtk_file_chooser_button_get_title ( --> Str )
[[gtk_] file_chooser_button_] set_title
Modifies the title of the browse dialog used by button.
method gtk_file_chooser_button_set_title ( Str $title )
- Str $title; the new browse dialog title.
[[gtk_] file_chooser_button_] get_width_chars
Retrieves the width in characters of the button widget’s entry and/or label.
Returns: an integer width (in characters) that the button will use to size itself.
method gtk_file_chooser_button_get_width_chars ( --> Int )
[[gtk_] file_chooser_button_] set_width_chars
Sets the width (in characters) that button will use to n_chars.
method gtk_file_chooser_button_set_width_chars ( Int $n_chars )
- Int $n_chars; the new width, in characters.
Signals
There are two ways to connect to a signal. The first option you have is to use register-signal() from Gnome::GObject::Object. The second option is to use g_signal_connect_object() directly from Gnome::GObject::Signal.
First method
The positional arguments of the signal handler are all obligatory as well as their types. The named attributes :$widget and user data are optional.
# handler method
method mouse-event ( GdkEvent $event, :$widget ) { ... }
# connect a signal on window object
my Gnome::Gtk3::Window $w .= new( ... );
$w.register-signal( self, 'mouse-event', 'button-press-event');
Second method
my Gnome::Gtk3::Window $w .= new( ... );
my Callable $handler = sub (
N-GObject $native, GdkEvent $event, OpaquePointer $data
) {
...
}
$w.connect-object( 'button-press-event', $handler);
Also here, the types of positional arguments in the signal handler are important. This is because both methods register-signal() and g_signal_connect_object() are using the signatures of the handler routines to setup the native call interface.
Supported signals
file-set
The file-set signal is emitted when the user selects a file.
Note that this signal is only emitted when the user changes the file.
Since: 2.12
method handler (
Int :$_handle_id,
Gnome::GObject::Object :_widget($widget),
*%user-options
);
- $widget; the object which received the signal.
Properties
An example of using a string type property of a Gnome::Gtk3::Label object. This is just showing how to set/read a property, not that it is the best way to do it. This is because a) The class initialization often provides some options to set some of the properties and b) the classes provide many methods to modify just those properties. In the case below one can use new(:label(‘my text label’)) or gtk_label_set_text(‘my text label’).
my Gnome::Gtk3::Label $label .= new;
my Gnome::GObject::Value $gv .= new(:init(G_TYPE_STRING));
$label.g-object-get-property( 'label', $gv);
$gv.g-value-set-string('my text label');
Supported properties
Dialog
Instance of the Gnome::Gtk3::FileChooserDialog associated with the button. Widget type: GTK_TYPE_FILE_CHOOSER
The Gnome::GObject::Value type of property dialog is G_TYPE_OBJECT.
Title
Title to put on the Gnome::Gtk3::FileChooserDialog associated with the button.
The Gnome::GObject::Value type of property title is G_TYPE_STRING.
Width In Characters
The width of the entry and label inside the button, in characters.
The Gnome::GObject::Value type of property width-chars is G_TYPE_INT.