Gnome::Gtk3::StyleContext
Rendering UI elements
Description
Gnome::Gtk3::StyleContext is an object that stores styling information affecting a widget.
In order to construct the final style information, Gnome::Gtk3::StyleContext queries information from all attached Gnome::Gtk3::StyleProviders. Style providers can be either attached explicitly to the context through add-provider(), or to the screen through add-provider-for-screen(). The resulting style is a combination of all providers’ information in priority order.
For GTK+ widgets, any Gnome::Gtk3::StyleContext returned by Gnome::Gtk3::Widget.get-style-context() will already have a Gnome::Gtk3::WidgetPath, a Gnome::Gdk3::Screen and RTL/LTR information set. The style context will also be updated automatically if any of these settings change on the widget.
If you are using the theming layer standalone, you will need to set a widget path and a screen yourself to the created style context through set_path() and set_screen().
Style Classes
Widgets can add style classes to their context, which can be used to associate different styles by class. The documentation for individual widgets lists which style classes it uses itself, and which style classes may be added by applications to affect their appearance.
GTK+ defines macros for a number of style classes.
Custom styling in UI libraries and applications
If you are developing a library with custom Gnome::Gtk3::Widgets that render differently than standard components, you may need to add a Gnome::Gtk3::StyleProvider yourself with the GTK_STYLE_PROVIDER_PRIORITY_FALLBACK priority, either a Gnome::Gtk3::CssProvider or a custom object implementing the Gnome::Gtk3::StyleProvider interface. This way themes may still attempt to style your UI elements in a different way if needed so.
If you are using custom styling on an application, you probably want then to make your style information prevail to the theme’s, so you must use a Gnome::Gtk3::StyleProvider with the GTK_STYLE_PROVIDER_PRIORITY_APPLICATION priority, keep in mind that the user settings in XDG_CONFIG_HOME/gtk-3.0/gtk.css will still take precedence over your changes, as it uses the GTK_STYLE_PROVIDER_PRIORITY_USER priority.
Synopsis
Declaration
unit class Gnome::Gtk3::StyleContext;
also is Gnome::GObject::Object;
Inheriting this class
Inheriting is done in a special way in that it needs a call from new() to get the native object created by the class you are inheriting from.
use Gnome::Gtk3::StyleContext;
unit class MyGuiClass;
also is Gnome::Gtk3::StyleContext;
submethod new ( |c ) {
# let the Gnome::Gtk3::StyleContext class process the options
self.bless( :GtkStyleContext, |c);
}
submethod BUILD ( ... ) {
...
}
Example
Types
GtkStyleContextPrintFlags
Flags that modify the behavior of gtk_style_context_to_string(). New values may be added to this enumeration.
-
GTK_STYLE_CONTEXT_PRINT_NONE;
-
GTK_STYLE_CONTEXT_PRINT_RECURSE; Print the entire tree of CSS nodes starting at the style context’s node
-
GTK_STYLE_CONTEXT_PRINT_SHOW_STYLE; Show the values of the CSS properties for each node
Methods
new
default, no options
Create a new plain object. The value doesn’t have to be True nor False. The name only will suffice.
multi method new ( )
:native-object
Create a StyleContext object using a native object from elsewhere. See also Gnome::N::TopLevelClassSupport.
multi method new ( N-GObject :$native-object! )
:build-id
Create a StyleContext object using a native object returned from a builder. See also Gnome::GObject::Object.
multi method new ( Str :$build-id! )
add-class
Adds a style class to context, so posterior calls to get() or any of the gtk-render-*() functions will make use of this new class for styling.
In the CSS file format, a Gnome::Gtk3::Entry defining a “search” class, would be matched by:
entry.search { … }
While any widget defining a “search” class would be matched by:
.search { … }
method add-class ( Str $class_name )
- Str $class_name; class name to use in styling
add-provider
Adds a style provider to context, to be used in style construction. Note that a style provider added by this function only affects the style of the widget to which context belongs. If you want to affect the style of all widgets, use add-provider-for-screen().
Note: If both priorities are the same, a Gnome::Gtk3::StyleProvider added through this function takes precedence over another added through add-provider-for-screen().
method add-provider ( N-GObject $provider, UInt $priority )
-
N-GObject $provider; a Gnome::Gtk3::StyleProvider
-
UInt $priority; the priority of the style provider. The lower it is, the earlier it will be used in the style construction. Typically this will be in the range between
GTK-STYLE-PROVIDER-PRIORITY-FALLBACKandGTK-STYLE-PROVIDER-PRIORITY-USER
add-provider-for-screen
Adds a global style provider to screen, which will be used in style construction for all Gnome::Gtk3::StyleContexts under screen.
GTK+ uses this to make styling information from Gnome::Gtk3::Settings available.
Note: If both priorities are the same, A Gnome::Gtk3::StyleProvider added through add-provider() takes precedence over another added through this function.
method add-provider-for-screen ( N-GObject $screen, N-GObject $provider, UInt $priority )
-
N-GObject $screen; a Gnome::Gtk3::Screen
-
N-GObject $provider; a Gnome::Gtk3::StyleProvider
-
UInt $priority; the priority of the style provider. The lower it is, the earlier it will be used in the style construction. Typically this will be in the range between
GTK-STYLE-PROVIDER-PRIORITY-FALLBACKandGTK-STYLE-PROVIDER-PRIORITY-USER
get-border, get-border-rk
Returns the border for a given state as a Gnome::Gtk3::Border.
method get-border ( UInt $state --> N-GtkBorder )
method get-border-rk ( UInt $state --> Gnome::Gtk3::Border )
- UInt $state; state flags from GtkStateFlags to retrieve the border for
get-color, get-color-rk
Returns the foreground color for a given state.
method get-color ( Uint $state --> N-GdkRGBA )
method get-color-rk ( UInt $state --> Gnome::Gdk3::RGBA )
- UInt $state; state flags from GtkStateFlags to retrieve the color for
get-junction-sides
Returns the sides where rendered elements connect visually with others.
Returns: the junction sides mask. Bits are from GtkJunctionSides.
method get-junction-sides ( --> UInt )
get-margin, get-margin-rk
Returns the margin for a given state as a Gnome::Gtk3::Border.
method get-margin ( UInt $state --> N-GtkBorder )
method get-margin-rk ( UInt $state --> Gnome::Gtk3::Border )
- UInt $state; state flags from GtkStateFlags to retrieve the border for
get-padding, get-padding-rk
Returns the padding for a given state as a Gnome::Gtk3::Border.
method get-padding ( UInt $state --> N-GtkBorder )
method get-padding-rk ( UInt $state --> Gnome::Gtk3::Border )
- UInt $state; state flags from GtkStateFlagsto retrieve the padding for
get-parent, get-parent-rk
Gets the parent context set via set-parent(). See that function for details.
Returns: the parent context or undefined
method get-parent ( --> N-GObject )
method get-parent-rk ( --> Gnome::Gtk3::StyleContext )
get-path, get-path-rk
Returns the widget path used for style matching.
Returns: A Gnome::Gtk3::WidgetPath
method get-path ( --> N-GObject )
method get-path-rk ( --> Gnome::Gtk3::WidgetPath )
get-scale
Returns the scale used for assets.
Returns: the scale
method get-scale ( --> Int )
get-screen, get-screen-rk
Returns the Gnome::Gtk3::Screen to which context is attached.
Returns: a Gnome::Gtk3::Screen.
method get-screen ( --> N-GObject )
method get-screen-rk ( --> Gnome::Gdk3::Screen )
get-section, get-section-rk
Queries the location in the CSS where $property was defined for the current context. Note that the state to be queried is taken from get-state().
If the location is not available, undefined will be returned. The location might not be available for various reasons, such as the property being overridden, $property not naming a supported CSS property or tracking of definitions being disabled for performance reasons.
Shorthand CSS properties cannot be queried for a location and will always return undefined.
Returns: undefined or the section where a value for $property was defined
method get-section ( Str $property --> N-GObject )
method get-section-rk ( Str $property --> Gnome::Gtk3::CssSection )
- $property; style property name
get-state
Returns the state used for style matching.
This method should only be used to retrieve the bit mask of GtkStateFlags to pass to Gnome::Gtk3::StyleContext methods, like get-padding(). If you need to retrieve the current state of a Gnome::Gtk3::Widget, use Gnome::Gtk3::Widget.get-state-flags().
Returns: the state flags bit mask from GtkStateFlags
method get-state ( --> UInt )
get-style-property, get-style-property-rk
Gets the value for a widget style property.
When value is no longer needed, g-value-unset() must be called to free any allocated memory.
method get-style-property ( Str $property_name --> N-GValue )
method get-style-property-rk ( Str $property_name --> Gnome::GObject::Value )
-
Str $property_name; the name of the widget style property
-
N-GObject $value; Return location for the property value
has-class
Returns True if context currently has defined the given class name.
Returns: True if context has class-name defined
method has-class ( Str $class_name --> Bool )
- Str $class_name; a class name
list-classes, list-classes-rk
Returns the list of classes currently defined in context.
Returns: a Gnome::Gtk3::List of strings with the currently defined classes. The contents of the list are owned by GTK+, but you must free the list itself with clear-object() when you are done with it.
method list-classes ( --> N-GList )
method list-classes-rk ( --> Gnome::Glib::List )
lookup-color, lookup-color-rk
Looks up and resolves a color name in the context color map.
Returns: N-GdkRGBA color if color-name was found and resolved, undefined or invalid otherwise
method lookup-color ( Str $color_name --> N-GdkRGBA )
method lookup-color-rk ( Str $color_name --> Gnome::Gdk3::RGBA )
- Str $color_name; color name to lookup
remove-class
Removes class-name from context.
method remove-class ( Str $class_name )
- Str $class_name; class name to remove
remove-provider
Removes provider from the style providers list in context.
method remove-provider ( N-GObject $provider )
- N-GObject $provider; a Gnome::Gtk3::StyleProvider
remove-provider-for-screen
Removes provider from the global style providers list in screen.
method remove-provider-for-screen ( N-GObject $screen, N-GObject $provider )
-
N-GObject $screen; a Gnome::Gtk3::Screen
-
N-GObject $provider; a Gnome::Gtk3::StyleProvider
render-activity
Renders an activity indicator (such as in Gnome::Gtk3::Spinner). The state GTK-STATE-FLAG-CHECKED determines whether there is activity going on.
method render-activity (
cairo_t $cr, Num() $x, Num() $y, Num() $width, Num() $height
)
-
cairo_t $cr; a cairo-t
-
Num() $x; X origin of the rectangle
-
Num() $y; Y origin of the rectangle
-
Num() $width; rectangle width
-
Num() $height; rectangle height
render-arrow
Renders an arrow pointing to angle.
Typical arrow rendering at 0, 1⁄2 π;, π; and 3⁄2 π:

method render-arrow (
cairo_t $cr, Num() $angle, Num() $x, Num() $y, Num() $size
)
-
cairo_t $cr; a cairo-t
-
Num() $angle; arrow angle from 0 to 2 *
G-PI, being 0 the arrow pointing to the north -
Num() $x; X origin of the render area
-
Num() $y; Y origin of the render area
-
Num() $size; square side for render area
render-background
Renders the background of an element.
Typical background rendering, showing the effect of background-image, border-width and border-radius:

method render-background (
cairo_t $cr, Num() $x, Num() $y, Num() $width, Num() $height
)
-
cairo_t $cr; a cairo-t
-
Num() $x; X origin of the rectangle
-
Num() $y; Y origin of the rectangle
-
Num() $width; rectangle width
-
Num() $height; rectangle height
render-background-get-clip
Returns the area that will be affected (i.e. drawn to) when calling background() for the given context and rectangle. Returns a N-GdkRectangle (defined in Gnome::Gdk3::Types).
method render-background-get-clip (
Num() $x, Num() $y, Num() $width, Num() $height --> N-GdkRectangle
)
-
Num() $x; X origin of the rectangle
-
Num() $y; Y origin of the rectangle
-
Num() $width; rectangle width
-
Num() $height; rectangle height
render-check
Renders a checkmark (as in a Gnome::Gtk3::CheckButton).
The GTK-STATE-FLAG-CHECKED state determines whether the check is on or off, and GTK-STATE-FLAG-INCONSISTENT determines whether it should be marked as undefined.
Typical checkmark rendering:

method render-check (
cairo_t $cr, Num() $x, Num() $y, Num() $width, Num() $height
)
-
cairo_t $cr; a cairo-t
-
Num() $x; X origin of the rectangle
-
Num() $y; Y origin of the rectangle
-
Num() $width; rectangle width
-
Num() $height; rectangle height
render-expander
Renders an expander (as used in Gnome::Gtk3::TreeView and Gnome::Gtk3::Expander) in the area defined by x, y, width, height. The state GTK-STATE-FLAG-CHECKED determines whether the expander is collapsed or expanded.
Typical expander rendering:

method render-expander (
cairo_t $cr, Num() $x, Num() $y, Num() $width, Num() $height
)
-
cairo_t $cr; a cairo-t
-
Num() $x; X origin of the rectangle
-
Num() $y; Y origin of the rectangle
-
Num() $width; rectangle width
-
Num() $height; rectangle height
render-extension
Renders a extension (as in a Gnome::Gtk3::Notebook tab) in the rectangle defined by x, y, width, height. The side where the extension connects to is defined by gap-side.
Typical extension rendering:

method render-extension (
cairo_t $cr, Num() $x, Num() $y, Num() $width, Num() $height,
GtkPositionType $gap_side
)
-
cairo_t $cr; a cairo-t
-
Num() $x; X origin of the rectangle
-
Num() $y; Y origin of the rectangle
-
Num() $width; rectangle width
-
Num() $height; rectangle height
-
GtkPositionType $gap_side; side where the gap is
render-focus
Renders a focus indicator on the rectangle determined by x, y, width, height.
Typical focus rendering:

method render-focus (
cairo_t $cr, Num() $x, Num() $y, Num() $width, Num() $height
)
-
cairo_t $cr; a cairo-t
-
Num() $x; X origin of the rectangle
-
Num() $y; Y origin of the rectangle
-
Num() $width; rectangle width
-
Num() $height; rectangle height
render-frame
Renders a frame around the rectangle defined by x, y, width, height.
Examples of frame rendering, showing the effect of border-image, border-color, border-width, border-radius and junctions:
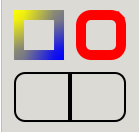
method render-frame (
cairo_t $cr, Num() $x, Num() $y, Num() $width, Num() $height
)
-
cairo_t $cr; a cairo-t
-
Num() $x; X origin of the rectangle
-
Num() $y; Y origin of the rectangle
-
Num() $width; rectangle width
-
Num() $height; rectangle height
render-handle
Renders a handle (as in Gnome::Gtk3::HandleBox, Gnome::Gtk3::Paned and Gnome::Gtk3::Window’s resize grip), in the rectangle determined by x, y, width, height.
Handles rendered for the paned and grip classes:

method render-handle (
cairo_t $cr, Num() $x, Num() $y, Num() $width, Num() $height
)
-
cairo_t $cr; a cairo-t
-
Num() $x; X origin of the rectangle
-
Num() $y; Y origin of the rectangle
-
Num() $width; rectangle width
-
Num() $height; rectangle height
render-icon
Renders the icon in pixbuf at the specified x and y coordinates.
This function will render the icon in pixbuf at exactly its size, regardless of scaling factors, which may not be appropriate when drawing on displays with high pixel densities.
You probably want to use icon-surface() instead, if you already have a Cairo surface.
method render-icon (
cairo_t $cr, N-GPixbuf $pixbuf, Num() $x, Num() $y
)
-
cairo_t $cr; a cairo-t
-
N-GObject $pixbuf; a Gnome::Gtk3::Pixbuf containing the icon to draw
-
Num() $x; X position for the pixbuf
-
Num() $y; Y position for the pixbuf
render-icon-surface
Renders the icon in surface at the specified x and y coordinates.
method render-icon-surface (
cairo_t $cr, cairo_surface_t $surface, Num() $x, Num() $y
)
-
cairo_t $cr; a cairo-t
-
cairo_surface_t $surface; a cairo-surface-t containing the icon to draw
-
Num() $x; X position for the icon
-
Num() $y; Y position for the incon
render-line
Renders a line from (x0, y0) to (x1, y1).
method render-line (
cairo_t $cr, Num() $x0, Num() $y0, Num() $x1, Num() $y1
)
-
cairo_t $cr; a cairo-t
-
Num() $x0; X coordinate for the origin of the line
-
Num() $y0; Y coordinate for the origin of the line
-
Num() $x1; X coordinate for the end of the line
-
Num() $y1; Y coordinate for the end of the line
render-option
Renders an option mark (as in a Gnome::Gtk3::RadioButton), the GTK-STATE-FLAG-CHECKED state will determine whether the option is on or off, and GTK-STATE-FLAG-INCONSISTENT whether it should be marked as undefined.
Typical option mark rendering:

method render-option (
cairo_t $cr, Num() $x, Num() $y, Num() $width, Num() $height
)
-
cairo_t $cr; a cairo-t
-
Num() $x; X origin of the rectangle
-
Num() $y; Y origin of the rectangle
-
Num() $width; rectangle width
-
Num() $height; rectangle height
render-slider
Renders a slider (as in Gnome::Gtk3::Scale) in the rectangle defined by x, y, width, height. orientation defines whether the slider is vertical or horizontal.
Typical slider rendering:

method render-slider (
cairo_t $cr, Num() $x, Num() $y, Num() $width, Num() $height,
GtkOrientation $orientation
)
-
cairo_t $cr; a cairo-t
-
Num() $x; X origin of the rectangle
-
Num() $y; Y origin of the rectangle
-
Num() $width; rectangle width
-
Num() $height; rectangle height
-
GtkOrientation $orientation; orientation of the slider
reset-widgets
This function recomputes the styles for all widgets under a particular Gnome::Gtk3::Screen. This is useful when some global parameter has changed that affects the appearance of all widgets, because when a widget gets a new style, it will both redraw and recompute any cached information about its appearance. As an example, it is used when the color scheme changes in the related Gnome::Gtk3::Settings object.
method reset-widgets ( N-GObject $screen )
- N-GObject $screen; a Gnome::Gtk3::Screen
restore
Restores context state to a previous stage. See save().
method restore ( )
save
Saves the context state, so temporary modifications done through add-class(), remove-class(), set-state(), etc. can quickly be reverted in one go through gtk-style-context-restore().
The matching call to gtk-style-context-restore() must be done before GTK returns to the main loop.
method save ( )
set-junction-sides
Sets the sides where rendered elements (mostly through render-frame()) will visually connect with other visual elements.
This is merely a hint that may or may not be honored by themes.
Container widgets are expected to set junction hints as appropriate for their children, so it should not normally be necessary to call this function manually.
method set-junction-sides ( UInt $sides )
- UInt $sides; sides where rendered elements are visually connected to other elements. Bits ae from GtkJunctionSides.
set-parent
Sets the parent style context for context. The parent style context is used to implement inheritance of properties.
If you are using a Gnome::Gtk3::StyleContext returned from gtk-widget-get-style-context(), the parent will be set for you.
method set-parent ( N-GObject $parent )
- N-GObject $parent; the new parent or
undefined
set-path
Sets the Gnome::Gtk3::WidgetPath used for style matching. As a consequence, the style will be regenerated to match the new given path.
If you are using a Gnome::Gtk3::StyleContext returned from Gnome::Gtk3::Widget.get-style-context(), you do not need to call this yourself.
method set-path ( N-GObject $path )
- N-GObject $path; a Gnome::Gtk3::WidgetPath
set-scale
Sets the scale to use when getting image assets for the style.
method set-scale ( Int() $scale )
- Int() $scale; scale
set-screen
Attaches context to the given screen.
The screen is used to add style information from “global” style providers, such as the screen’s Gnome::Gtk3::Settings instance.
If you are using a Gnome::Gtk3::StyleContext returned from gtk-widget-get-style-context(), you do not need to call this yourself.
method set-screen ( N-GObject $screen )
- N-GObject $screen; a Gnome::Gtk3::Screen
set-state
Sets the state bit mask to be used for style matching.
method set-state ( UInt $flags )
- UInt $flags; state to represent using bits from GtkStateFlags
to-string
Converts the style context into a string representation.
The string representation always includes information about the name, state, id, visibility and style classes of the CSS node that is backing context. Depending on the flags, more information may be included.
This function is intended for testing and debugging of the CSS implementation in GTK+. There are no guarantees about the format of the returned string, it may change.
Returns: a newly allocated string representing context
method to-string ( Uint $flags --> Str )
- UInt $flags; Flags that determine what to print. Nits are from GtkStyleContextPrintFlags
Signals
There are two ways to connect to a signal. The first option you have is to use register-signal() from Gnome::GObject::Object. The second option is to use connect-object() directly from Gnome::GObject::Signal.
First method
The positional arguments of the signal handler are all obligatory as well as their types. The named attributes :$widget and user data are optional.
# handler method
method mouse-event ( GdkEvent $event, :$widget ) { ... }
# connect a signal on window object
my Gnome::Gtk3::Window $w .= new( ... );
$w.register-signal( self, 'mouse-event', 'button-press-event');
Second method
my Gnome::Gtk3::Window $w .= new( ... );
my Callable $handler = sub (
N-GObject $native, GdkEvent $event, OpaquePointer $data
) {
...
}
$w.connect-object( 'button-press-event', $handler);
Also here, the types of positional arguments in the signal handler are important. This is because both methods register-signal() and connect-object() are using the signatures of the handler routines to setup the native call interface.
Supported signals
changed
The changed signal is emitted when there is a change in the Gnome::Gtk3::StyleContext.
For a Gnome::Gtk3::StyleContext returned by Gnome::Gtk3::Widget.get-style-context(), the style-updated signal might be more convenient to use.
This signal is useful when using the theming layer standalone.
method handler (
Int :$_handle_id,
Gnome::Gtk3::StyleContext :$_widget,
*%user-options
);
-
$_handle_id; the registered event handler id
-
$_widget; the object which received the signal.
Properties
An example of using a string type property of a Gnome::Gtk3::Label object. This is just showing how to set/read a property, not that it is the best way to do it. This is because a) The class initialization often provides some options to set some of the properties and b) the classes provide many methods to modify just those properties. In the case below one can use new(:label(‘my text label’)) or .set-text(‘my text label’).
my Gnome::Gtk3::Label $label .= new;
my Gnome::GObject::Value $gv .= new(:init(G_TYPE_STRING));
$label.get-property( 'label', $gv);
$gv.set-string('my text label');
Supported properties
Direction: direction
Text direction Default value: False
The Gnome::GObject::Value type of property direction is G_TYPE_ENUM.
FrameClock: paint-clock
The associated GdkFrameClock Widget type: GDK-TYPE-FRAME-CLOCK
The Gnome::GObject::Value type of property paint-clock is G_TYPE_OBJECT.
Parent: parent
Sets or gets the style context’s parent. See set-parent() for details.
Widget type: GTK_TYPE_STYLE_CONTEXT
The Gnome::GObject::Value type of property parent is G_TYPE_OBJECT.
Screen: screen
The associated GdkScreen Widget type: GDK-TYPE-SCREEN
The Gnome::GObject::Value type of property screen is G_TYPE_OBJECT.