Gnome::Gtk3::Menu
A menu widget
Description
A Gnome::Gtk3::Menu is a Gnome::Gtk3::MenuShell that implements a drop down menu consisting of a list of Gnome::Gtk3::MenuItem objects which can be navigated and activated by the user to perform application functions.
A Gnome::Gtk3::Menu is most commonly dropped down by activating a Gnome::Gtk3::MenuItem in a Gnome::Gtk3::MenuBar or popped up by activating a Gnome::Gtk3::MenuItem in another Gnome::Gtk3::Menu.
A Gnome::Gtk3::Menu can also be popped up by activating a Gnome::Gtk3::ComboBox. Other composite widgets such as the Gnome::Gtk3::Notebook can pop up a Gnome::Gtk3::Menu as well.
Applications can display a Gnome::Gtk3::Menu as a popup menu by calling the gtk_menu_popup() function. The example below shows how an application can pop up a menu when the 3rd mouse button is pressed.
Connecting the popup signal handler.
class HandlerClass {
method popup-handler (
N-GdkEvent $event, Gnome::Gtk3::Window :widget($window), :$menu
--> Int
) {
my Int $ret-value = 0;
if $event.event-any.type ~~ GDK_BUTTON_PRESS {
my N-GdkEventButton $event-button = $event;
if $event-button.button ~~ GDK_BUTTON_SECONDARY {
$menu.pop-at-widget(
$window, GDK_GRAVITY_SOUTH, GDK_GRAVITY_CENTER, $event
);
$ret-value = 1;
}
}
$ret-value
}
}
# Setup the menu
my Gnome::Gtk3::Menu $menu .= new;
...
# Create a window and register a handler for the button press signal
my Gnome::Gtk3::Window $w .= new(:title('My Window'));
$w.register-signal(
HandlerClass.new, 'popup-handler', 'button_press_event', :$menu
);
Css Nodes
menu
├── arrow.top
├── <child>
┊
├── <child>
╰── arrow.bottom
The main CSS node of Gnome::Gtk3::Menu has name menu, and there are two subnodes with name arrow, for scrolling menu arrows. These subnodes get the .top and .bottom style classes.
Synopsis
Declaration
unit class Gnome::Gtk3::Menu;
also is Gnome::Gtk3::MenuShell;
Types
enum GtkArrowPlacement
Used to specify the placement of scroll arrows in scrolling menus.
-
GTK_ARROWS_BOTH: Place one arrow on each end of the menu.
-
GTK_ARROWS_START: Place both arrows at the top of the menu.
-
GTK_ARROWS_END: Place both arrows at the bottom of the menu.
Methods
new
Create a new plain object.
multi method new ( )
Create an object using a native object from elsewhere. See also Gnome::GObject::Object.
multi method new ( N-GObject :$native-object! )
Create an object using a native object from a builder. See also Gnome::GObject::Object.
multi method new ( Str :$build-id! )
[[gtk_] menu_] popup_at_rect
Displays $menu and makes it available for selection.
See gtk_menu_popup_at_widget() and gtk_menu_popup_at_pointer(), which handle more common cases for popping up menus.
The menu will be positioned at $rect, aligning their anchor points. $rect is relative to the top-left corner of $rect_window. $rect_anchor and $menu_anchor determine anchor points on $rect and $menu to pin together. $menu can optionally be offset by $rect-anchor-dx and $rect-anchor-dy.
Anchors should be specified under the assumption that the text direction is left-to-right; they will be flipped horizontally automatically if the text direction is right-to-left.
Other properties that influence the behaviour of this function are anchor-hints and menu-type-hint. Connect to the popped-up signal to find out how it was actually positioned.
method gtk_menu_popup_at_rect (
N-GObject $rect_window, N-GdkRectangle $rect,
GdkGravity $rect_anchor, GdkGravity $menu_anchor,
N-GdkEvent $trigger_event
)
-
N-GObject $rect_window; the Gnome::Gdk3::Window $rect is relative to
-
N-GObject $rect; the Gnome::Gdk3::Rectangle to align the menu with
-
GdkGravity $rect_anchor; the point on $rect to align with menu’s anchor point
-
GdkGravity $menu_anchor; the point on menu to align with rect’s anchor point
-
N-GdkEvent $trigger_event; the Gnome::Gdk3::Event that initiated this request or undefined if it’s the current event
[[gtk_] menu_] popup_at_widget
Displays the menu and makes it available for selection.
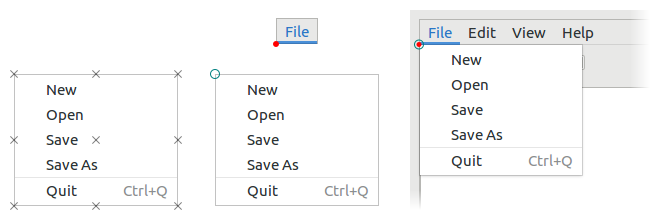
The menu will be positioned at $widget, aligning their anchor points. $widget_anchor and $menu_anchor determine anchor points on $widget and the menu to pin together.
Anchors should be specified under the assumption that the text direction is left-to-right; they will be flipped horizontally automatically if the text direction is right-to-left.
Other properties that influence the behaviour of this function are anchor-hints and menu-type-hint. Connect to the popped-up signal to find out how it was actually positioned.
method gtk_menu_popup_at_widget (
N-GObject $widget, GdkGravity $widget_anchor,
GdkGravity $menu_anchor, N-GdkEvent $trigger_event
)
-
N-GObject $widget; the widget to align the menu with
-
GdkGravity $widget_anchor; the point on $widget to align with the menu’s anchor point
-
GdkGravity $menu_anchor; the point on the menu to align with $widget’s anchor point
-
N-GdkEvent $trigger_event; (nullable): the N-GdkEvent that initiated this request or
Anyif it’s the current event
[gtk_] menu_reposition
Repositions the menu according to its position function.
method gtk_menu_reposition ( )
[gtk_] menu_popdown
Removes the menu from the screen.
method gtk_menu_popdown ( )
[[gtk_] menu_] get_active
Returns the selected menu item from the menu. This is used by the Gnome::Gtk3::ComboBox.
Returns: (transfer none): the Gnome::Gtk3::MenuItem that was last selected in the menu. If a selection has not yet been made, the first menu item is selected.
method gtk_menu_get_active ( --> N-GObject )
[[gtk_] menu_] set_active
Selects the specified menu item within the menu. This is used by the Gnome::Gtk3::ComboBox and should not be used by anyone else.
method gtk_menu_set_active ( UInt $index )
- UInt $index; the index of the menu item to select. Index values are from 0 to n-1
[[gtk_] menu_] set_accel_group
Set the Gnome::Gtk3::AccelGroup which holds global accelerators for the menu. This accelerator group needs to also be added to all windows that this menu is being used in with gtk_window_add_accel_group(), in order for those windows to support all the accelerators contained in this group.
method gtk_menu_set_accel_group ( N-GObject $accel_group )
- N-GObject $accel_group; (allow-none): the Gnome::Gtk3::AccelGroup to be associated with the menu.
[[gtk_] menu_] get_accel_group
Gets the Gnome::Gtk3::AccelGroup which holds global accelerators for the menu. See gtk_menu_set_accel_group().
Returns: (transfer none): the Gnome::Gtk3::AccelGroup associated with the menu
method gtk_menu_get_accel_group ( --> N-GObject )
[[gtk_] menu_] set_accel_path
Sets an accelerator path for this menu from which accelerator paths for its immediate children, its menu items, can be constructed. The main purpose of this function is to spare the programmer the inconvenience of having to call gtk_menu_item_set_accel_path() on each menu item that should support runtime user changable accelerators. Instead, by just calling gtk_menu_set_accel_path() on their parent, each menu item of this menu, that contains a label describing its purpose, automatically gets an accel path assigned.
For example, a menu containing menu items “New” and “Exit”, will, after gtk_menu_set_accel_path (menu, "<Gnumeric-Sheet>/File"); has been called, assign its items the accel paths: "<Gnumeric-Sheet>/File/New" and "<Gnumeric-Sheet>/File/Exit".
Assigning accel paths to menu items then enables the user to change their accelerators at runtime. More details about accelerator paths and their default setups can be found at gtk_accel_map_add_entry().
Note that accel_path string will be stored in a GQuark. Therefore, if you pass a static string, you can save some memory by interning it first with g_intern_static_string().
method gtk_menu_set_accel_path ( Str $accel_path )
- Str $accel_path; (allow-none): a valid accelerator path
[[gtk_] menu_] get_accel_path
Retrieves the accelerator path set on the menu.
Returns: the accelerator path set on the menu.
method gtk_menu_get_accel_path ( --> Str )
[gtk_] menu_detach
Detaches the menu from the widget to which it had been attached. This function will call the callback function, detacher, provided when the gtk_menu_attach_to_widget() function was called.
method gtk_menu_detach ( )
[[gtk_] menu_] get_attach_widget
Returns the Gnome::Gtk3::Widget that the menu is attached to.
Returns: (transfer none): the Gnome::Gtk3::Widget that the menu is attached to
method gtk_menu_get_attach_widget ( --> N-GObject )
[[gtk_] menu_] reorder_child
Moves child to a new position in the list of menu children.
method gtk_menu_reorder_child ( N-GObject $child, Int $position )
-
N-GObject $child; the Gnome::Gtk3::MenuItem to move
-
Int $position; the new position to place child. Positions are numbered from 0 to n - 1
[[gtk_] menu_] set_screen
Sets the Gnome::Gdk3::Screen on which the menu will be displayed.
method gtk_menu_set_screen ( N-GObject $screen )
- N-GObject $screen; (allow-none): a Gnome::Gdk3::Screen, or
Anyif the screen should be determined by the widget the menu is attached to
[gtk_] menu_attach
Adds a new Gnome::Gtk3::MenuItem to a (table) menu. The number of “cells” that an item will occupy is specified by left_attach, right_attach, top_attach and bottom_attach. These each represent the leftmost, rightmost, uppermost and lower column and row numbers of the table. (Columns and rows are indexed from zero).
Note that this function is not related to gtk_menu_detach().
method gtk_menu_attach ( N-GObject $child, UInt $left_attach, UInt $right_attach, UInt $top_attach, UInt $bottom_attach )
-
N-GObject $child; a Gnome::Gtk3::MenuItem
-
UInt $left_attach; The column number to attach the left side of the item to
-
UInt $right_attach; The column number to attach the right side of the item to
-
UInt $top_attach; The row number to attach the top of the item to
-
UInt $bottom_attach; The row number to attach the bottom of the item to
[[gtk_] menu_] set_monitor
Informs GTK+ on which monitor a menu should be popped up. See gdk_monitor_get_geometry().
This function should be called from a Gnome::Gtk3::MenuPositionFunc if the menu should not appear on the same monitor as the pointer. This information can’t be reliably inferred from the coordinates returned by a Gnome::Gtk3::MenuPositionFunc, since, for very long menus, these coordinates may extend beyond the monitor boundaries or even the screen boundaries.
method gtk_menu_set_monitor ( Int $monitor_num )
- Int $monitor_num; the number of the monitor on which the menu should be popped up
[[gtk_] menu_] get_monitor
Retrieves the number of the monitor on which to show the menu.
Returns: the number of the monitor on which the menu should be popped up or -1, if no monitor has been set
method gtk_menu_get_monitor ( --> Int )
[[gtk_] menu_] place_on_monitor
method gtk_menu_place_on_monitor ( N-GObject $monitor )
- N-GObject $monitor;
[[gtk_] menu_] get_for_attach_widget
Returns a list of the menus which are attached to this widget. This list is owned by GTK+ and must not be modified.
Returns: (element-type Gnome::Gtk3::Widget) (transfer none): the list of menus attached to his widget.
method gtk_menu_get_for_attach_widget ( N-GObject $widget --> N-GList )
- N-GObject $widget; a Gnome::Gtk3::Widget
[[gtk_] menu_] set_reserve_toggle_size
Sets whether the menu should reserve space for drawing toggles or icons, regardless of their actual presence.
method gtk_menu_set_reserve_toggle_size ( Int $reserve_toggle_size )
- Int $reserve_toggle_size; whether to reserve size for toggles
[[gtk_] menu_] get_reserve_toggle_size
Returns whether the menu reserves space for toggles and icons, regardless of their actual presence.
Returns: Whether the menu reserves toggle space
method gtk_menu_get_reserve_toggle_size ( --> Int )
Signals
There are two ways to connect to a signal. The first option you have is to use register-signal() from Gnome::GObject::Object. The second option is to use g_signal_connect_object() directly from Gnome::GObject::Signal.
First method
The positional arguments of the signal handler are all obligatory as well as their types. The named attributes :$widget and user data are optional.
# handler method
method mouse-event ( N-GdkEvent $event, :$widget ) { ... }
# connect a signal on window object
my Gnome::Gtk3::Window $w .= new( ... );
$w.register-signal( self, 'mouse-event', 'button-press-event');
Second method
my Gnome::Gtk3::Window $w .= new( ... );
my Callable $handler = sub (
N-GObject $native, N-GdkEvent $event, OpaquePointer $data
) {
...
}
$w.connect-object( 'button-press-event', $handler);
Also here, the types of positional arguments in the signal handler are important. This is because both methods register-signal() and g_signal_connect_object() are using the signatures of the handler routines to setup the native call interface.
Supported signals
move-scroll
method handler (
Unknown type GTK_TYPE_SCROLL_TYPE $scroll_type,
Int :$_handler_id,
Gnome::GObject::Object :_widget($menu),
*%user-options
);
-
$menu; a Gnome::Gtk3::Menu
-
$scroll_type; a Gnome::Gtk3::ScrollType
popped-up
Emitted when the position of menu is finalized after being popped up using gtk_menu_popup_at_rect(), gtk_menu_popup_at_widget(), or gtk_menu_popup_at_pointer().
menu might be flipped over the anchor rectangle in order to keep it on-screen, in which case flipped_x and flipped_y will be set to 1 accordingly.
flipped_rect is the ideal position of menu after any possible flipping, but before any possible sliding. final_rect is flipped_rect, but possibly translated in the case that flipping is still ineffective in keeping menu on-screen.
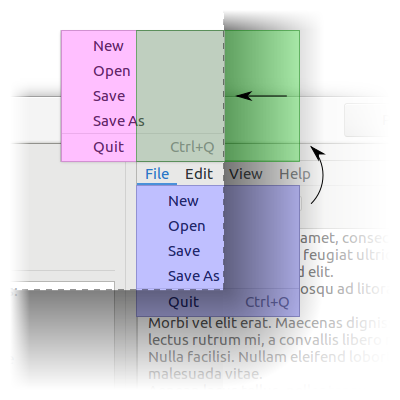
The blue menu is menu’s ideal position, the green menu is flipped_rect, and the red menu is final_rect.
See gtk_menu_popup_at_rect(), gtk_menu_popup_at_widget(), gtk_menu_popup_at_pointer(), anchor-hints, rect-anchor-dx, rect-anchor-dy, and menu-type-hint.
method handler (
Unknown type G_TYPE_POINTER $flipped_rect,
Unknown type G_TYPE_POINTER $final_rect,
Int $flipped_x,
Int $flipped_y,
Int :$_handler_id,
Gnome::GObject::Object :_widget($menu),
*%user-options
);
-
$menu; the Gnome::Gtk3::Menu that popped up
-
$flipped_rect; (nullable): the position of menu after any possible flipping or
Anyif the backend can’t obtain it -
$final_rect; (nullable): the final position of menu or
Anyif the backend can’t obtain it -
$flipped_x;
1if the anchors were flipped horizontally -
$flipped_y;
1if the anchors were flipped vertically
Properties
An example of using a string type property of a Gnome::Gtk3::Label object. This is just showing how to set/read a property, not that it is the best way to do it. This is because a) The class initialization often provides some options to set some of the properties and b) the classes provide many methods to modify just those properties. In the case below one can use new(:label(‘my text label’)) or gtk_label_set_text(‘my text label’).
my Gnome::Gtk3::Label $label .= new;
my Gnome::GObject::Value $gv .= new(:init(G_TYPE_STRING));
$label.g-object-get-property( 'label', $gv);
$gv.g-value-set-string('my text label');
Supported properties
Active
The index of the currently selected menu item, or -1 if no menu item is selected.
The Gnome::GObject::Value type of property active is G_TYPE_INT.
Accel Group
The accel group holding accelerators for the menu.
Widget type: GTK_TYPE_ACCEL_GROUP
The Gnome::GObject::Value type of property accel-group is G_TYPE_OBJECT.
Accel Path
An accel path used to conveniently construct accel paths of child items.
The Gnome::GObject::Value type of property accel-path is G_TYPE_STRING.
Attach Widget
The widget the menu is attached to. Setting this property attaches the menu without a Gnome::Gtk3::MenuDetachFunc. If you need to use a detacher, use gtk_menu_attach_to_widget() directly.
Widget type: GTK_TYPE_WIDGET
The Gnome::GObject::Value type of property attach-widget is G_TYPE_OBJECT.
Monitor
The monitor the menu will be popped up on.
The Gnome::GObject::Value type of property monitor is G_TYPE_INT.
Reserve Toggle Size
A boolean that indicates whether the menu reserves space for toggles and icons, regardless of their actual presence. This property should only be changed from its default value for special-purposes such as tabular menus. Regular menus that are connected to a menu bar or context menus should reserve toggle space for consistency.
The Gnome::GObject::Value type of property reserve-toggle-size is G_TYPE_BOOLEAN.
Anchor hints
Positioning hints for aligning the menu relative to a rectangle. These hints determine how the menu should be positioned in the case that the menu would fall off-screen if placed in its ideal position. 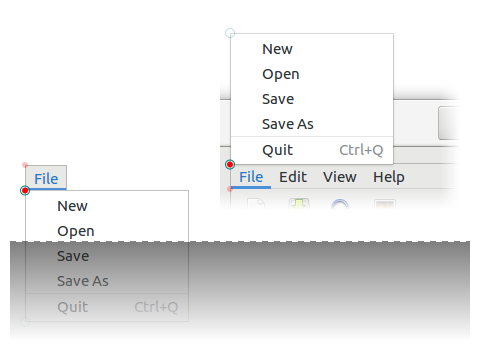 For example,
For example, GDK_ANCHOR_FLIP_Y will replace GDK_GRAVITY_NORTH_WEST with GDK_GRAVITY_SOUTH_WEST and vice versa if the menu extends beyond the bottom edge of the monitor. See gtk_menu_popup_at_rect(), gtk_menu_popup_at_widget(), gtk_menu_popup_at_pointer(), rect-anchor-dx, rect-anchor-dy, menu-type-hint, and popped-up.
The Gnome::GObject::Value type of property anchor-hints is G_TYPE_FLAGS.
Rect anchor dx
Horizontal offset to apply to the menu, i.e. the rectangle or widget anchor. See gtk_menu_popup_at_rect(), gtk_menu_popup_at_widget(), gtk_menu_popup_at_pointer(), anchor-hints, rect-anchor-dy, menu-type-hint, and popped-up.
The Gnome::GObject::Value type of property rect-anchor-dx is G_TYPE_INT.
Rect anchor dy
Vertical offset to apply to the menu, i.e. the rectangle or widget anchor. See gtk_menu_popup_at_rect(), gtk_menu_popup_at_widget(), gtk_menu_popup_at_pointer(), anchor-hints, rect-anchor-dx, menu-type-hint, and popped-up.
The Gnome::GObject::Value type of property rect-anchor-dy is G_TYPE_INT.
Menu type hint
The Gnome::Gdk3::WindowTypeHint to use for the menu’s Gnome::Gdk3::Window. See gtk_menu_popup_at_rect(), gtk_menu_popup_at_widget(), gtk_menu_popup_at_pointer(), anchor-hints, rect-anchor-dx, rect-anchor-dy, and popped-up. Widget type: GDK_TYPE_WINDOW_TYPE_HINT
The Gnome::GObject::Value type of property menu-type-hint is G_TYPE_ENUM.